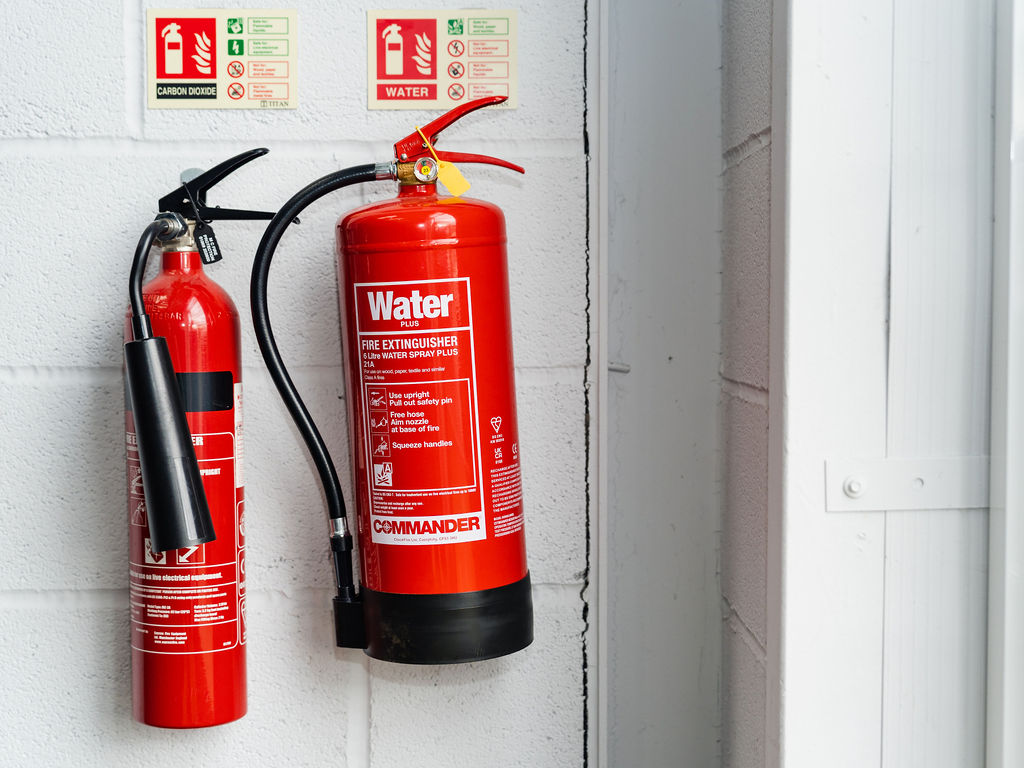
Fire Extinguishers
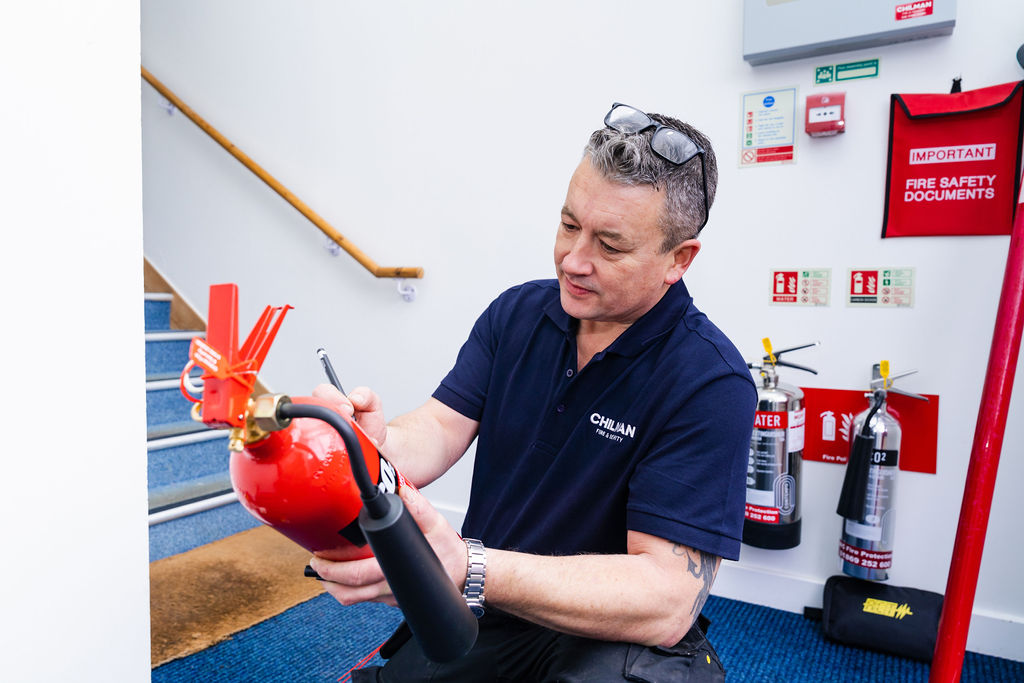
Our highly skilled BAFE registered technicians, can service, install and commission all types of Fire Extinguishers. Our team will identify and explain exactly what is needed to provide the correct fire rating for your premises.
Classes of Fire
Fires are divided into classes depending on the type of material that is burning, and different fire extinguishers are used to tackle each different class of fire. So, when installing fire extinguishers on your premises it is essential to consider the level of risk of each class of fire that your building poses. This can be ascertained through a fire risk assessment.
The different classes of fire are:
Class A – involves the combustion of organic materials such as wood, paper and fabric. Class A fires tend to be the most common type of fire.
Class B – involves the combustion of flammable liquids such as petrol, oil, paraffin, alcohol and certain paints.
Class C – involves flammable gases such as butane and propane as well as natural gases that are used when cooking or heating a building.
Electrical – involves electrical equipment.
Class F – often referred to as kitchen fires because they primarily involve cooking or vegetable oils
| Type of Fire Extinguisher | Fire Classification | Fire Extinguisher Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| ABC POWDER |   | Powder fire extinguishers: ideal for use in mixed-risk environments and offer excellent all-around fire protection. |
| AFF FOAM |   | Foam fire extinguishers: excellent for use on fires involving solid, flammable materials and are very efficient on liquid fires. |
| CARBON DIOXIDE |   | CO2 fire extinguishers: suitable for use on flammable liquid fires and are remarkably efficient at extinguishing a fire involving electrical equipment. |
| WATER |   | Water fire extinguishers: useful in situations that contain solid, flammable materials such as textiles, wood or paper. |
| WATER MIST |   | Water mist extinguishers: perfect for covering building spaces where multiple fire risks can be found. |
| WET CHEMICAL |   | Wet chemical extinguishers: the perfect solution for tackling large burning oil fires and also ideally suited to the kitchen environment. |
Main Fire Extinguisher Categories









Fire Extinguishers
Get in touch with the team to get a quote
Our team will be happy to help with any queries you may have. We offer free no obligation site visits, to ensure you're getting the best possible advice and option for you and your property
